Accessing the EGP
The English Grammar Profile is available as a free, online resource, through the English Profile website. Please note that the Terms Of Use for this resource do not allow other organisations to promote commercial materials as “English Profile informed” without written permission from the English Profile core network members.
For more detailed guidance on searching the EGP, please download our user guide.
How to search the EGP
The are two ways to search the EGP: simple searches, and advanced searches. A simple search allows you to search the whole dataset for your key word, e.g. "permission":
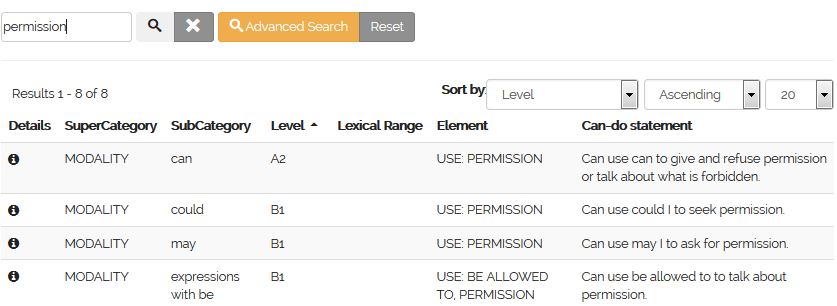
An advanced search allows you to filter your search results by grammatical categories and CEFR level.
What's in the EGP?
Each entry in the EGP dataset corresponds to an element of grammatical competence. When you conduct a search, your results will appear as a table, with one row for every element:

Each row contains information in some or all of the following fields:
Element: an individual aspect of grammatical competence; these fall into three sub-types:
- Form: this entry concerns grammatical form, e.g.

- Use: this entry concerns different specific uses of a grammatical form, e.g.

- Form/Use: this entry indicates both form and use, where the particular form is rarely used for any other purpose, e.g.

Super Category: the broad category of the grammatical element, e.g. adjectives, clauses, modality, negations, reported speech etc.
Sub Category: a narrower category of the grammatical element, e.g. comparatives, future in the past, might, uncountable etc.
Level: the CEFR level at which the element is typically mastered.
Lexical Range: the lexical development within the grammatical feature, indicating limited/increasing/wide vocabulary with bar chart icons.
Can-do statement: the can-do statement associated with the grammatical element, e.g. can use but to join a limited range of common adjectives, after be.
As well as the fields above, you can access more detailed information by clicking on the "i" icon in the "Details" column. Each entry contains some or all of the following information:
- Corrected learner examples: examples of the element taken from the CLC and modified, where necessary, so that they are “expert speaker like”.
- Uncorrected learner examples: examples of the element taken directly from the CLC. These examples may contain learner errors.
- Comments: alert the user to limitations with the data, e.g. that there may not be enough data to provide sufficient evidence for the feature, or that a different type of data (e.g. spoken) may be needed.






